Resonators, general susceptibility, and AC effects
General resonator
Assume the driving force have the form
Equation of motion
with a response of form , we get
General susceptibility
General susceptibility is defined as
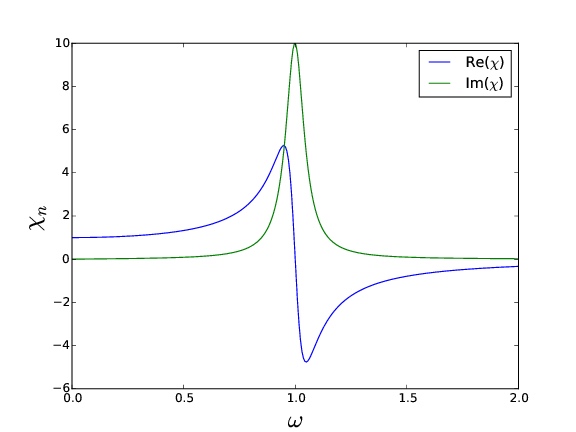
- Imaginary part ()
- Symmetric, gaussian function
- FWHM
- Real part ()
- Antisymmetric
- when
- when
Q-factor, or quality factor
Q-factor relate to the imaginary part, or the term=
Phase
The phase of the response is defined by
Kramers-Kronig relations
General stimulus and general response
Power consumption
measures the power absorbed per unit space.